nosql-manager-for-mongoDB数据查询用法
最近因为一些原因,不得不直接进数据库改数据,于是有了这篇博客。
在MongoDB中,Query、Projection和Order是常用的查询操作,分别用于筛选数据、指定返回字段和排序结果。
以下是详细的介绍和用法:
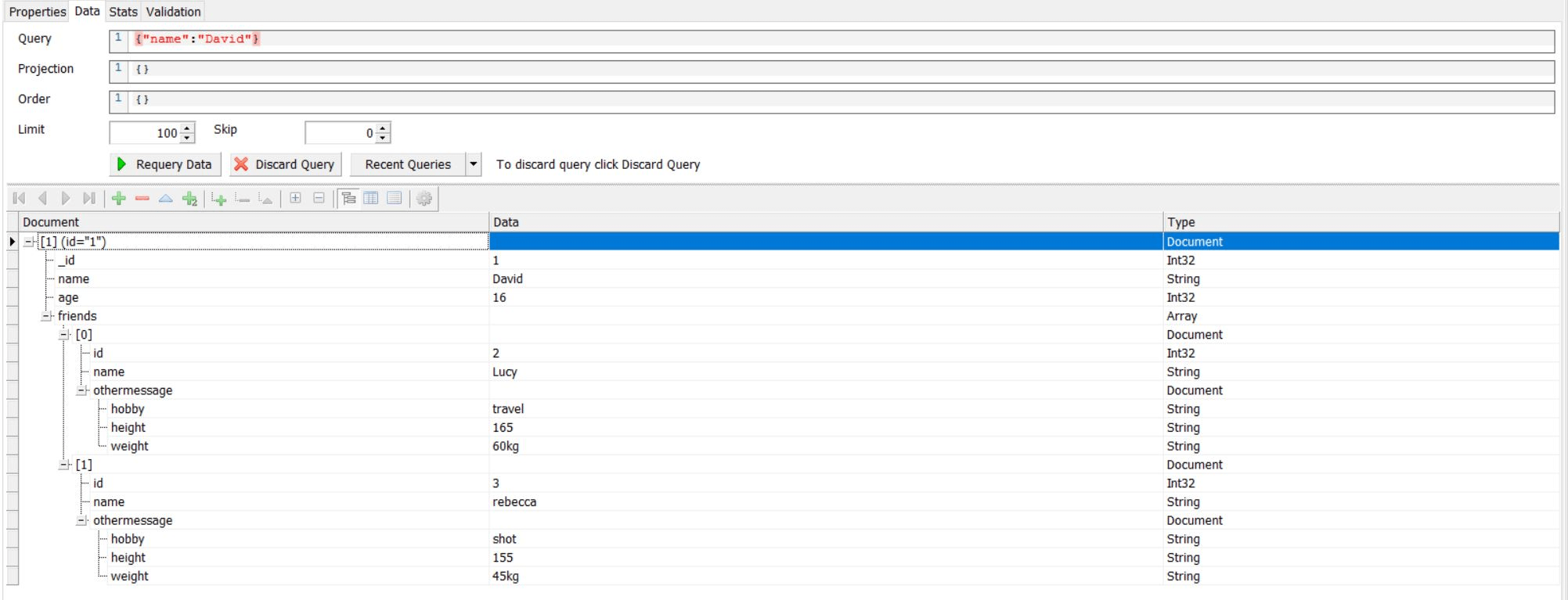
假设表中存在以下结构的数据:
1 | |
Query(查询)
Query用于指定查询条件,以筛选集合中的文档。可以使用各种条件运算符来构建查询。
查询特定字段的文档:
{"name":"David"}返回name为David的整条条目
使用比较运算符:
{"age":{$gt:20}}返回age大于25的整条条目
常用的比较运算符有:
$eq(等于)
示例:
{"age":{$eq:20}}$ne(不等于)
示例:
{"age":{$ne:20}}$gt(大于)
示例:
{"age":{$gt:20}}$gte(大于或等于)
示例:
{"age":{$gte:20}}$lt(小于)
示例:
{"age":{$lt:20}}$lte(小于或等于)
示例:
{"age":{$lte:20}}$in(在数组中)
示例:
{"age":{$in:[25,30,35]}}$nin(不在数组中)
示例:
{"age":{$in:[25,30,35]}}
查询嵌套字段:
{"friends.name":"alice"}返回friends.name为alice的整条条目
查询数组中的元素
{"interests":"reading"}返回interests里包含reading的整条条目
Projection(投影)
Projection用于指定查询结果中应包含或排除的字段,可以在查询中使用投影来返回必要的字段
包含特定的字段
1
2Query:{"name":"yamako"}
Projection:{"name":1,"age":1}只返回name和age字段,其他字段不显示
id是比较特殊的字段,默认会显示,除非加上”_id”:0
排除特定的字段
1
2Query:{"name":"yamako"}
Projection:{"age":0}返回文档时排除age字段
查询嵌套字段
对于三层嵌套结构来说,由于GUI界面可操作性较小,这里选择了使用shell工具来实现聚合管道
示例:
假设要查询到兴趣为旅行的人,且只显示姓名,朋友的姓名以及朋友的爱好,其他字段都不显示,那么需要做的是:
- 使用 $unwind 操作符先展开数组
- 使用 $match 操作符来匹配兴趣爱好是旅行的人
- 使用 $project 操作符来显示姓名,朋友的姓名以及朋友的还好,并隐藏 _id
- 将上面三条通过 db.collection,aggregate 方法聚合起来
示例代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5db.People.aggregate([
{$unwind:"$friends"},
{$match:{"friends.othermessage.hobby":"travel"}},
{$project:{"_id":0,"name":1,"friends.name":1,"friends.othermessage.hobby":1}}
])最后返回的结果是:只有David的朋友Lucy爱好是旅行,且只显示了三条字段,和预期结果一致
Order(排序)
按单个字段升序排序:
{"age":1}按age字段升序排序
按单个字段降序排序:
{"age":-1}按age字段降序排序
按多个字段排序:
{"age":1,"friends.name":-1}先按age字段升序排序,再按朋友的名字friends.name降序排序